1.1 View绘制流程
View绘制流程与原理
- 绘制起点
ViewRootImpl#performTraversals()
mView.measure();
// measure核心关键流程
// 1. onMeasure
// 2. setMeasuredDimension
// 3. 根据Mode返回size, 如是MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED则返回mMinWidth/mMinHeight, 否则返回父类传入大小,
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY //确定模式,父View希望子View的大小是确定的,由specSize决定;
MeasureSpec.AT_MOST //最多模式,父View希望子View的大小最多是specSize指定的值;
MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED //未指定模式,父View完全依据子View的设计值来决定;
// 4. measureChild -> measureChildWidthMargins
// 5. getChildMeasureSpec的逻辑是通过其父View提供的MeasureSpec参数得到specMode和specSize,然后根据计算出来的specMode以及子View的childDimension(layout_width或layout_height)来计算自身的measureSpec
mView.layout();
// 1. onLayout
// 2. layoutVertical [LinearLayout]
// 3. 获取子View的LayoutParams
// 4. 循环排布, 并设置子View的位置
mView.draw();
// 1. 绘制背景
// 2. View内容绘制
// 3. 子View的绘制
// 4. 滚动条绘制
// 单独讲下mView#invalidate()
mView.invalidate();
// 1. 设置刷新区域
// 2. 调用parent#invalidateChild
// 3. 层层往上直到ViewRootImpl
-
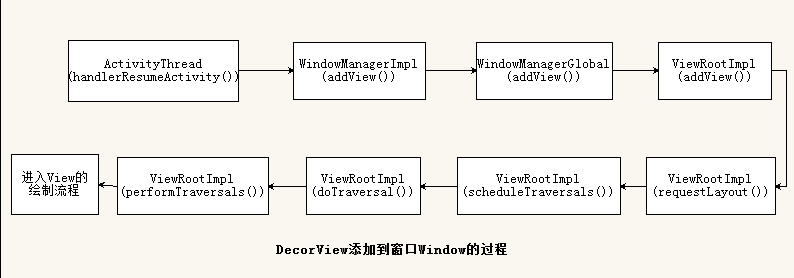
从
ActivityThread#handleResumeActivity()到ViewRootImpl分析View的绘制流程图, 图片来自从ViewRootImpl类分析View绘制的流程 -
直接分析
ViewRootImpl#performTraversals()
private void performTraversals() {
...
// mWidth和mHeight表示窗口宽高, lp.width和lp.height表示DecorView根布局宽和高
int childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mWidth, lp.width);
int childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mHeight, lp.height);
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
...
performLayout(desiredWindowWidth, desiredWindowHeight);
...
performDraw();
}
// 由于DecorView根布局测量模式为EXACTLY, 即测量大小为整个屏幕带下
private static int getRootMeasureSpec(int windowSize, int rootDimension) {
int measureSpec;
switch (rootDimension) {
// 测量模式为EXACTLY, 测量大小为屏幕大小
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT:
// Window can't resize. Force root view to be windowSize.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
// 测量模式为AT_MOST, 测量大小为屏幕大小
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT:
// Window can resize. Set max size for root view.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
break;
default:
// 测量模式为EXACTLY, 测量大小为DecorView顶层视图布局设置的大小
// Window wants to be an exact size. Force root view to be that size.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(rootDimension, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
}
return measureSpec;
}
performMeasure()
private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) {
...
mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
...
}
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
...
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
...
}
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
//获得测量模式
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
//获得父亲容器留给子视图View的大小
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
// MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED //未指定模式,父View完全依据子View的设计值来决定;
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
// MeasureSpec.EXACTLY //确定模式,父View希望子View的大小是确定的,由specSize决定;
// MeasureSpec.AT_MOST //最多模式,父View希望子View的大小最多是specSize指定的值;
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
DecorView继承于FrameLayout, 了解DecorView#onMeasure()实现
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
...
// 测量子View的宽和高
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
...
// 设置当前测量的结果
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState),
resolveSizeAndState(maxHeight, heightMeasureSpec,
childState << MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
}
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child,
int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin
+ widthUsed, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin
+ heightUsed, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
...
switch (specMode) {
// Parent has imposed an exact size on us
// 父容器为EXACTLY模式, 子View指定childDimension(dp、px)则使用子View设置大小,
// 子View若为MATCH_PARENT, 则使用父容器大小, 若子View为WRAP_CONTENT, 则大小为父容器大小
// 且resultMode设置为AT_MOST
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size. So be it.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... so be it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent asked to see how big we want to be
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... let him have it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should
// be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how
// big it should be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
}
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}
-
performLayout()private void performLayout(WindowManager.LayoutParams lp, int desiredWindowWidth, int desiredWindowHeight) { // DecorView请求布局 host.layout(0, 0, host.getMeasuredWidth(), host.getMeasuredHeight()); } // 看下View.java#layout() public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) { ... //设置当前View的位置,并且判断布局是否有改变 boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ? setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b); // 调用onLayout, 子类负责实现 onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b); ... } protected boolean setFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { ... //判断本次View的宽高和上次View的宽高是否相等 boolean sizeChanged = (newWidth != oldWidth) || (newHeight != oldHeight); // Invalidate our old position // 清楚上次布局的位置 invalidate(sizeChanged); //保存当前View的最新位置 mLeft = left; mTop = top; mRight = right; mBottom = bottom; ... //如果当前View的尺寸有所变化 if (sizeChanged) { sizeChange(newWidth, newHeight, oldWidth, oldHeight); } ... return changed; } // 由于View的onLayout空实现, 直接查看DecorView#onLayout实现, 即FrameLayout#onLayout实现 @Override protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { layoutChildren(left, top, right, bottom, false /* no force left gravity */); } void layoutChildren(int left, int top, int right, int bottom, boolean forceLeftGravity) { final int count = getChildCount(); final int parentLeft = getPaddingLeftWithForeground(); final int parentRight = right - left - getPaddingRightWithForeground(); final int parentTop = getPaddingTopWithForeground(); final int parentBottom = bottom - top - getPaddingBottomWithForeground(); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { final View child = getChildAt(i); if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) { final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams(); final int width = child.getMeasuredWidth(); final int height = child.getMeasuredHeight(); ... final int layoutDirection = getLayoutDirection(); final int absoluteGravity = Gravity.getAbsoluteGravity(gravity, layoutDirection); final int verticalGravity = gravity & Gravity.VERTICAL_GRAVITY_MASK; // 获取子View的四个方向 switch (absoluteGravity & Gravity.HORIZONTAL_GRAVITY_MASK) { case Gravity.CENTER_HORIZONTAL: childLeft = parentLeft + (parentRight - parentLeft - width) / 2 + lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin; break; case Gravity.RIGHT: if (!forceLeftGravity) { childLeft = parentRight - width - lp.rightMargin; break; } case Gravity.LEFT: default: childLeft = parentLeft + lp.leftMargin; } switch (verticalGravity) { case Gravity.TOP: childTop = parentTop + lp.topMargin; break; case Gravity.CENTER_VERTICAL: childTop = parentTop + (parentBottom - parentTop - height) / 2 + lp.topMargin - lp.bottomMargin; break; case Gravity.BOTTOM: childTop = parentBottom - height - lp.bottomMargin; break; default: childTop = parentTop + lp.topMargin; } // 调用子View的layout child.layout(childLeft, childTop, childLeft + width, childTop + height); } } } -
performDraw()
private boolean drawSoftware(Surface surface, AttachInfo attachInfo, int xoff, int yoff,
boolean scalingRequired, Rect dirty) {
...
// 调用View#draw, 开始绘制
mView.draw(canvas);
...
}
- MeasureSpec,
LayoutParams需要和父容器才能决定View的MeasureSpec- MeasureSpec.EXACTLY //确定模式,父View希望子View的大小是确定的,由specSize决定;
- MeasureSpec.AT_MOST //最多模式,父View希望子View的大小最多是specSize指定的值;
- MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED //未指定模式,父View完全依据子View的设计值来决定;