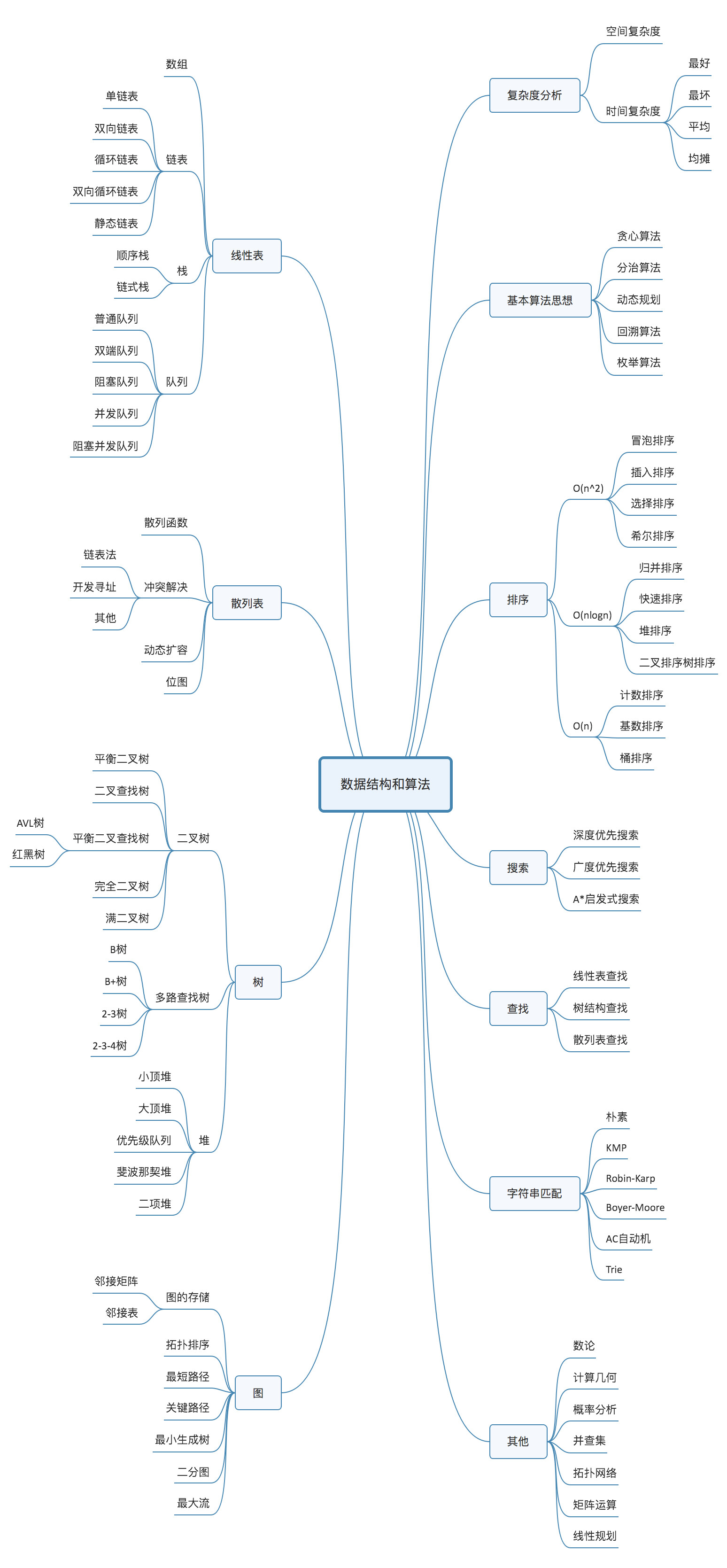
7.5 数据结构与算法
数据结构
Java数据结构
- List
- LinkedList, 链表实现
- Vector, 数组实现, 读写安全, 通过
synchronized实现
- 栈(Stack)
- Set
- LinkedHashSet
- HashSet, 使用
HashMap实现
- 二叉树
- 满二叉树, 除了叶子节点, 其它节点均有两个子节点
- 完全二叉树, 叶子结点只可能在层次最大的两层出现且前k-1层的结点是”满”的, 第k层的结点集中在左边
- 二叉树的遍历
- 先序遍历, 根结点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树; 例子结果: 1 2 4 5 7 8 3 6
- 中序遍历, 左子树 -> 根结点 -> 右子树; 例子结果: 4 2 7 5 8 1 3 6
- 后序遍历, 左子树 -> 右子树 -> 根结点; 例子结果: 4 7 8 5 2 6 3 1
- 层次遍历, 按层次遍历; 例子结果: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
- 二叉平衡树(AVL树), 即左右子树高度差不超过1(高度平衡, 频繁插入和删除, 会引起频繁的rebalance, 导致效率下降)
- 旋转(失去平衡包含左左, 右右, 左右, 右左四种情况)
- 左左型

public AVLNode<K,V> rotateLL(AVLNode<K,V> node) { // 把node的left结点作为根结点 var top = node.left // 截断原来的node.left, 并把top结点(新的根结点)的右子结点作为node.left结点 node.left = top.right; // 原来的根结点(node)作为top结点的右结点 top.right = node; // 重新结算高度 node.height = Math.Max(Height(node.left, Height(node.right)) + 1; top.height = Math.Max(Height(top.left), Height(top.right)) + 1; return top; } - 右右型

public AVLNode<K,V> rotateRR(AVLNode<K,V> node) { // 类似rotateLL, 不多解释 var top = node.right; node.right = top.left; top.left = node; // 重新结算高度 ... return top; } - 左右型

public AVLNode<K,V> rotateLR(AVLNode<K,V> node) { // 先右右旋转 node.left = rotateRR(node.left); // 再左左旋转 return rotateLL(node); } - 右左型

public AVLNode<K,V> rotateRL(AVLNode<K,V> node) { // 先左左旋转 node.right = rotateLL(node.right); // 再右右旋转 return rotateRR(node); }
- 左左型
- 插入
public AVLNode<K,V> add(K key, V value, AVLNode<K, V> tree) { if (tree == null) { tree = new AVLNode<K, V>(key, value, null, null); } if (key.CompareTo(tree.key) < 0) { // 找到不断往左遍历, 找到可插入点 tree.left = add(key, value, tree.left); if (Height(tree.left) - Height(tree.right) == 2) { // 左左型, key小于tree.left.key, 说明key放到tree.left的左边 if (key.CompareTo(tree.left.key) < 0) { tree = rotateLL(tree); } else { tree = rotateLR(tree); } } } if (key.CompareTo(tree.key) > 0) { tree.right = add(key, value, tree.right); if (Height(tree.right) - Height(tree.left) == 2) { if (key.CompareTo(tree.right.key) > 0) { tree = rotateRR(tree); } else { tree = rotateRL(tree); } } } if (key.CompareTo(tree.key) == 0) { tree.attach.add(value); } //计算高度 tree.height = Math.Max(Height(tree.left), Height(tree.right)) + 1; return tree; }
- 旋转(失去平衡包含左左, 右右, 左右, 右左四种情况)
- 红黑树 (非高度平衡, 插入最多旋转2次, 删除旋转3次)
- 特性
- 结点要么红要么黑
- 根结点是黑的
- 每个叶子结点(叶结点即树尾端NIL指针)都是黑的
- 如果一个结点是红的, 它的两个子结点均是黑的
- 对于任意结点, 到叶子结点的路径包含相同数量的黑结点
-
左旋
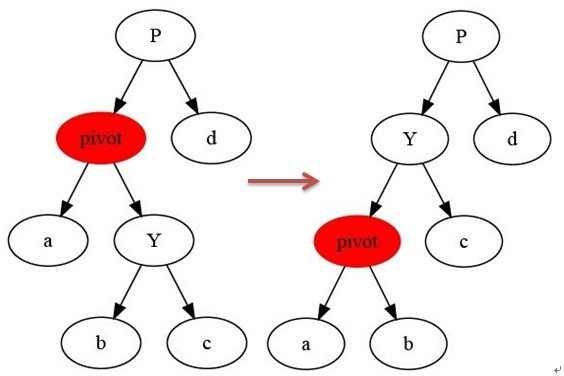
LeftRoate(T, x) y <- x.right; x.right <- y.left; if(y.left != Nil) y.left.parent <- x; y.parent <- x.parent; if x.parent == Nil then T.root <- y; else if x == x.parent.left then x.parent.left <- y; else x.parent.right <- y; y.left <- x; x.parent <- y; - 右旋

RightRoate(T, x) y <- x.left; x.left <- y.right; if(y.right != Nil) y.right.parent <- x; y.parent <- x.parent; if x.parent == Nil then T.root <- y else if x == x.parent.right then x.parent.right <- y; else x.parent.left <- y; y.right <- x; x.parent <- y; -
插入
- 删除
- 特性
- 堆
- 符合安全二叉树且父结点比子结点大(或小), 根结点最大的堆则叫做最大堆,根节点最小的堆则叫做最小堆
- B树
- B+树
- B*树
算法
排序算法
- 冒泡排序 O(N^2)
public void bubbleSort(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null) {
return ;
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < nums.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if(nums[j] > nums[j + 1]) {
int tmp = nums[j];
nums[j] = nums[j + 1];
nums[j + 1] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
- 插入排序 O(N^2), 平均情况下插入排序需要n*(n-1)/4
public void insertSort(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null) {
return ;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int temp = nums[i];
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && nums[j] > temp) {
nums[j + 1] = nums[j];
j--;
}
nums[j+1] = temp;
}
}
- 选择排序 O(N^2), 平均情况下选择排序需要n*(n-1)/2
public void selectionSort(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null) {
return ;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int minNum = nums[i];
int minIndex = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < nums.length; j++) {
if(nums[j] < minNum) {
minNum = nums[j];
minIndex = j;
}
}
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = minNum;
nums[minIndex] = temp;
}
}
- 快速排序(O(nlg(n)))
public void quickSort(int nums[], int low, int high) {
if(low < hight) {
int partition = partition(nums, low, high);
quickSort(nums, low, partition - 1);
quickSort(nums, partition + 1, high);
}
}
public int partition(int nums[], int low, int high) {
int pivot = nums[low];
while (low < high) {
while (low < high && nums[high] > pivot) {
high--;
}
nums[low] = nums[high];
while (low < high && nums[low] <= pivot) {
low++;
}
nums[high] = nums[low];
}
num[low] = pivot;
return low;
}
- 归并排序(O(nlg(n)))
public void mergeSort(int nums[], int left, int right, temp[]) {
if (left < right) {
int mid = (left + right)/2;
mergeSort(nums, left, mid, temp);
mergeSort(nums, mid + 1, right, temp);
merge(nums, left, mid, right, temp);
}
}
public void merge(int nums[], int left, int mid, int right, int temp[]) {
int i = left;
int j = mid + 1;
int t = 0;
while (i <= mid && j <= right) {
if (arr[i] <= arr[j]) {
temp[t++] = arr[i++];
} else {
temp[t++] = arr[j++];
}
}
while (i <= mid) {
temp[t++] = arr[i++];
}
while (j <= right) {
temp[t++] = arr[j++];
}
t = 0;
while(left <= right) {
arr[left++] = temp[t++];
}
}
- 堆排序(O(nlg(n)))
// parent = (child - 1) / 2
// leftChild = parent * 2 + 1; rightChild = parent * 2 + 2;
public void heapSort(int nums[]) {
// 1. 构建最大/最小堆
int len = nums.length;
buildHeap(nums, len);
// 根结点和最后的叶子结点交换, 并不断继续构建堆, 再交换, 最终得出来有序数组
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// 叶子结点和根结点交换
swap(nums, i, 0);
heapify(nums, i, 0);
}
}
private void swap(int nums[], int i, int j) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
private void buildHeap(int nums[], int len) {
int parentOfLastLeaf = (len - 1) / 2;
// 从最后叶子结点的父结点开始堆化, 构建堆
for (int i = parentOfLastLeaf; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(nums, len, i);
}
}
private void heapify(int nums[], int len, int i) {
if (i >= len) return;
int leftChild = 2 * i + 1;
int rightChild = 2 * i + 2;
int max = i;
if (leftChild < len && nums[leftChild] > nums[max]) {
max = leftChild;
}
if (rightChild < len && nums[rightChild] > nums[max]) {
max = rightChild;
}
if (max != i) {
swap(nums, max, i);
heapify(num, len, max);
}
}
查找算法
- 顺序查找(适合)
public int search(int nums[], int targetNumber) {
int targetIndex = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length ; i++) {
if (nums[i] == targetNumber) {
targetIndex = i;
break;
}
}
return targetIndex;
}
- 二分查找
public int binarySearch(int[] array, int searchKey) {
int low = 0;
int high = array.length;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (searchKey == array[mid]) {
return mid;
} else if (searchKey > array[mid]) {
low = mid + 1;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
- 插值查找
- 斐波那契查找
基本算法思想
- 贪心算法, 基本思想, 把问题拆解成N个小问题, 再根据小问题取最优解, 即局部最优解; 缺点: 1. 不能保证全局最优, 2. 不能求解最大或最小解问题
- 分治算法, 基本思想, 把复杂问题分成两个或多个相似的子问题, 直到最后子问题可以简单求解, 元问题的解即子问题的解的合并, 经典问题场景: 二分搜索, 快排, 归并排序等, 包含以下特征:
- 问题的规模缩小到一定程度可以容易解决
- 问题可以分解为若干小问题, 即该问题具有最优子结构性质
- 分解的子问题的解可以合并为该问题的解(能否使用分治算法的关键)
- 分解的子问题互相独立, 即子问题之间不包含公共的子子问题
- 动态规划(将一个问题拆成多个子问题, 分别求解这些子问题, 即可推断大问题的解)
- 无后性, 即给定某一阶段的状态, 则这一阶段的状态以后的过程不受以前状态的影响
- 最优子结构, 即大问题的最优解可以由小问题的最优解推出
- 重复子问题
- 解决思路
- 状态转移表法, 一般动态规划解决的问题都可以用回溯算法的暴力搜索解决, 即可用回溯算法解决, 定义状态, 每个状态即一个结点, 画出递归树, 从递归树看是否存在重复子问题, 子问题如何产生, 以此寻找规律, 最后决定是否使用动态规划
- 状态转移方程法, 写出递归公式, 即状态转移方程, 一般情况下, 1). 递归加”备忘录”, 2). 迭代递归
- 设计, 对于状态x, 记我们要求出的答案(e.g.最小费用)为f(x), 我们的目标是f(T), 找出f(x)与哪些局面有关(记为P), 写出一个式子(称为状态转移方程), 通过f(p)来推倒(fx)
- 动态规划三连, 即我是谁?->设计状态, 表示局面, 我从哪里来?, 我要到哪里去? -> 设计转移
- 回溯算法, 基本思想, 按照深度优先搜索的策略, 从根结点出发深度探索解空间树, 当探索到结点时, 先判断该结点是否包含问题的解, 如果包含就从该结点继续往下探索, 否则将逐层向其祖先结点回溯。
-
枚举算法, 基本思想, 把问题一一列举, 答案合适则保留, 否则舍弃
- TopK算法, 基本思想是堆排序, 根据K限定对堆进行增加删除
- 滑动窗口, 解决数组/字符串的子元素的问题, 解决嵌套循环, 转换为单循环问题, 降低复杂度, 可以解决查找最大/最小k子阵列,XOR,乘积,求和等问题
- KMP算法, 基本思想寻找字符串第i个字符与和模式串串的前缀/后缀集合交集的最大元素的长度, 即部分匹配表(Partial Match Table)数组. 易懂教程
public int kmpSearch(String originString, String matchString) {
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int next[] = getNext(originString, matchString);
while (i < originString.length() && j < matchString.length()) {
if (j == -1 || originString.indexOf(i).equals(matchString.indexOf(j))) {
i++;
j++;
} else {
j = next[i];
}
}
if (j > 0) {
return i - j;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
public int[] getNext(String originString, String matchString) {
int[] next = new int[originString.length()];
next[0] = -1;
int i = 0;
int j = -1;
while (i < originString.length) {
if (j == -1 || originString.indexOf(i).equals(matchString.indexOf(j))) {
i++;
j++;
next[i] = j;
} else {
j = next[j];
}
}
return next;
}
算法知识表